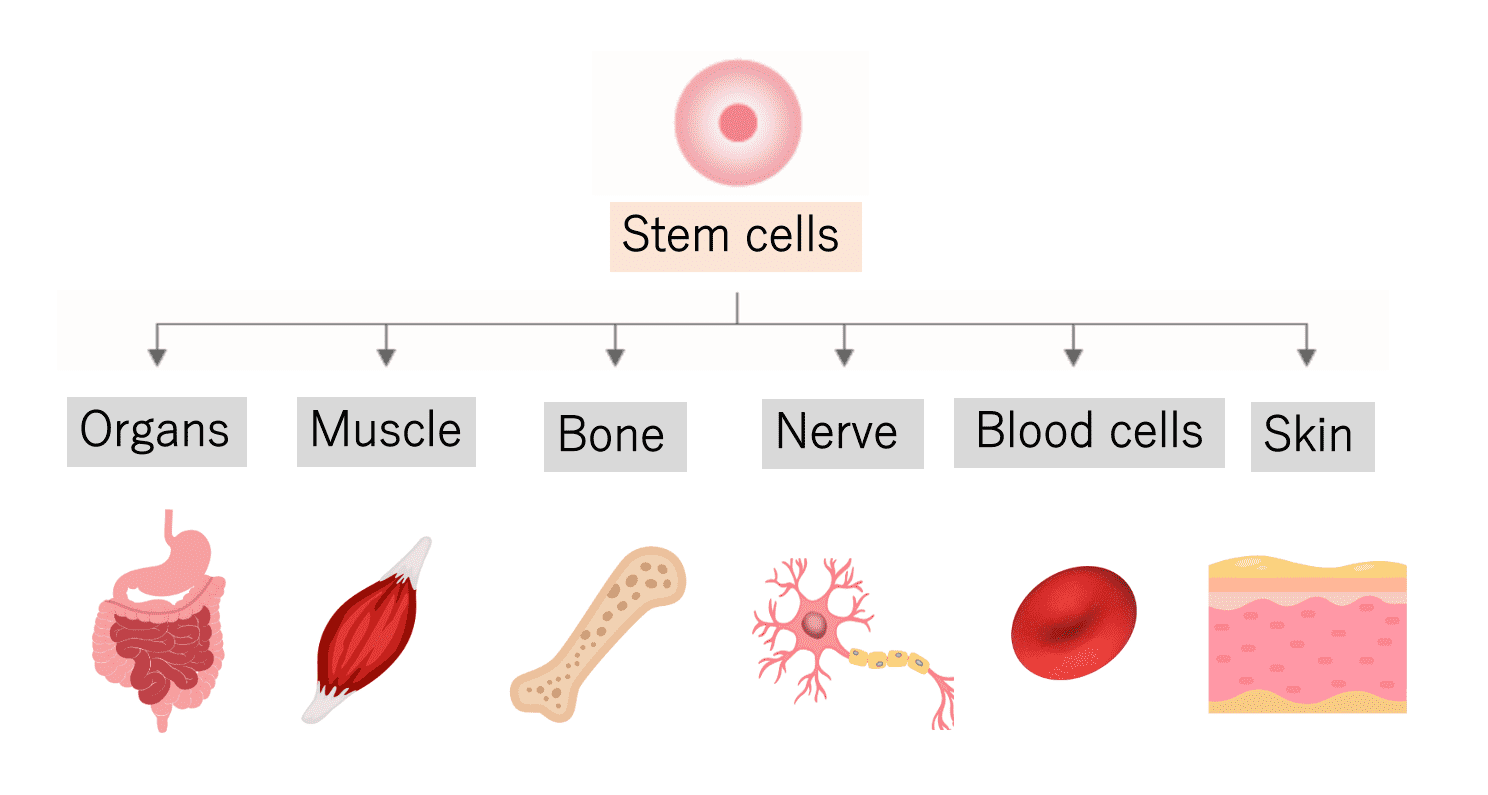
Regenerative medicine is a type of medical treatment that aims to improve or repair organs and tissues that have suffered from dysfunction or failure by transplanting cultured and proliferated stem cells into the body. Stem cells have the ability to produce new cells to replenish tissues that constantly renew their cells, such as the skin and blood. Primarily, stem cells possess two key abilities: the ability to replicate themselves by dividing (self-renewal) and the ability to differentiate into different types of cells (differentiation potential). Stem cells can be classified into pluripotent stem cells and somatic stem cells. The representative of pluripotent stem cells is induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), while the representative of somatic stem cells is mesenchymal stem cells. Cell therapy using mesenchymal stem cells, which are directly administered into the body, has already been commercialized in many fields. These mesenchymal stem cells can be harvested from various human tissues, including bone marrow, umbilical cord, and fat.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells extracted from adipose tissue have the ability to replenish cells lost due to disease or injury. Adipose-derived stem cells possess a homing effect, meaning they can travel through blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, seeking out damaged areas and migrating toward them for repair and regeneration. Additionally, these stem cells have the ability to regulate immune and inflammatory abnormalities, restoring them to normal (immunomodulatory effect), and can secrete various functional substances that influence neighboring cells (paracrine effect).